Blog
WHAT IS EFFECTIVE COMMUNICATION?
- December 15, 2024
- Posted by: Tripti Garg

“Communication works for those who work at it.” -John Powell
Has this ever happened to you, that while rehearsing a presentation alone, you could deliver it fluently, but once you stood in front of your peers, you found yourself at a loss for words?
Do you sometimes struggle to articulate ideas that are crystal clear in your mind, only to feel frustrated when you cannot express them effectively? Have you ever wondered how different things could have been if you had found the right words to communicate your thoughts effectively?
If so, you are not alone. According to LinkedIn’s 2023 Workforce Report, a significant skills gap persists, particularly in “timeless” soft skills such as adaptability, teamwork, and effective communication. Employers often say that while technical skills can often be taught, the absence of strong communication skills is a recurring issue in hiring.
This blog explores the art of effective communication, covering the different aspects, including its characteristics, applications, benefits, challenges, and practical strategies to help you master it.
What is effective communication?
Effective communication is the art of expressing your ideas and thoughts with clarity and proper articulation, ensuring that the other listener perceives your message or idea as intended.
Developing effective communication skills requires clarity, choosing the right words and tone, understanding the context, and being mindful of the environment.
It also involves emotional intelligence, confidence, and an awareness of body kinesics, that is, the nonverbal clues that complement verbal communication.
True effective communication occurs when there is mutual respect, patience, open-mindedness, and a willingness to embrace new ideas and constructive criticism. It thrives in an environment where individuals are receptive to feedback and ready to adapt accordingly.
Why is effective communication important?
Effective communication is essential for building strong personal and professional relationships. It helps you create a network and foster connections, opening doors to new opportunities for professional growth and enhancing leadership skills. This, in turn, enables individuals to grow and work on themselves.
Effective communication has applications in all essential areas in life.
In the Workplace: Effective communication is pivotal when seeking jobs or collaborating on projects. Articulating your skills clearly can have a lasting impression on potential employers, increasing the prospect of you getting the job. Within a team, strong communication fosters a healthy environment, facilitates task delegation, and encourages mutual support, enhancing productivity and collaboration.
In Education: Effective communication enriches the learning process, whether in school, college, or lifelong learning. Asking clarifying questions, exchanging constructive feedback, and engaging in discussions make learning more interactive, productive, and meaningful.
In Personal Relationships: Open and judgment-free communication strengthens bonds of trust and reliance, fostering supportive relationships. It allows individuals to express their feelings, resolve conflicts, and build mutual understanding.
In Public Settings: If you are a public speaker or host, effective communication ensures a confident and engaging presence. Using clear, concise language, appropriate gestures, and connecting with the audience creates a lasting impression, keeping listeners captivated until the end.
By mastering effective communication, you unlock the ability to connect, influence, and thrive in every sphere of life.
7 C’s of Effective Communication
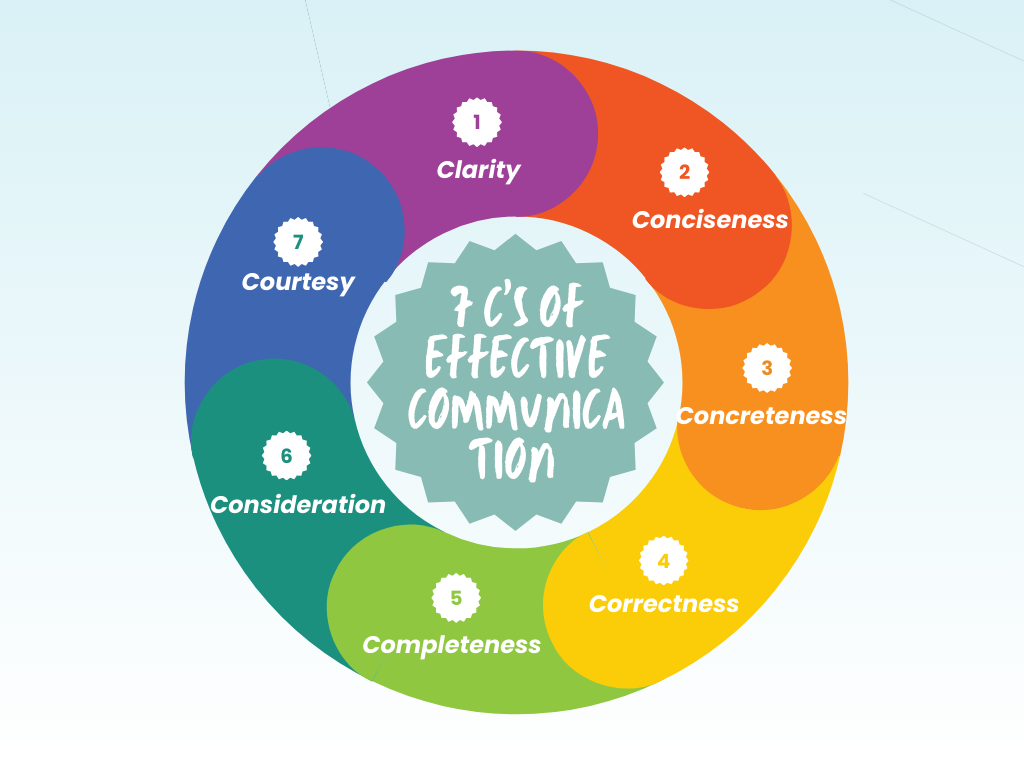
- Clarity: Ensure the message or information is clear and easily understood by the listener. Use simple language and avoid complex sentence structures to prevent confusion.
- Conciseness: Be direct and to the point. Eliminate unnecessary details and include only relevant information.
- Concreteness: Maintain the quality of the message by being specific and precise. Use concrete words to keep the focus on the core message.
- Correctness: Ensure that your communication is accurate, with no grammatical, factual, or technical errors.
- Completeness: Provide all necessary information, leaving no room for ambiguity or vagueness.
- Consideration: Understand and respect your audience’s background, viewpoints, and level of expertise. Tailor your message accordingly.
- Courtesy: Communicate with respect and courtesy. Avoid harsh or passive-aggressive tones, and maintain an open and honest approach.
These 7 C’s form the foundation of mastering effective communication, ensuring your message is impactful and well received.
What are the benefits of effective communication?
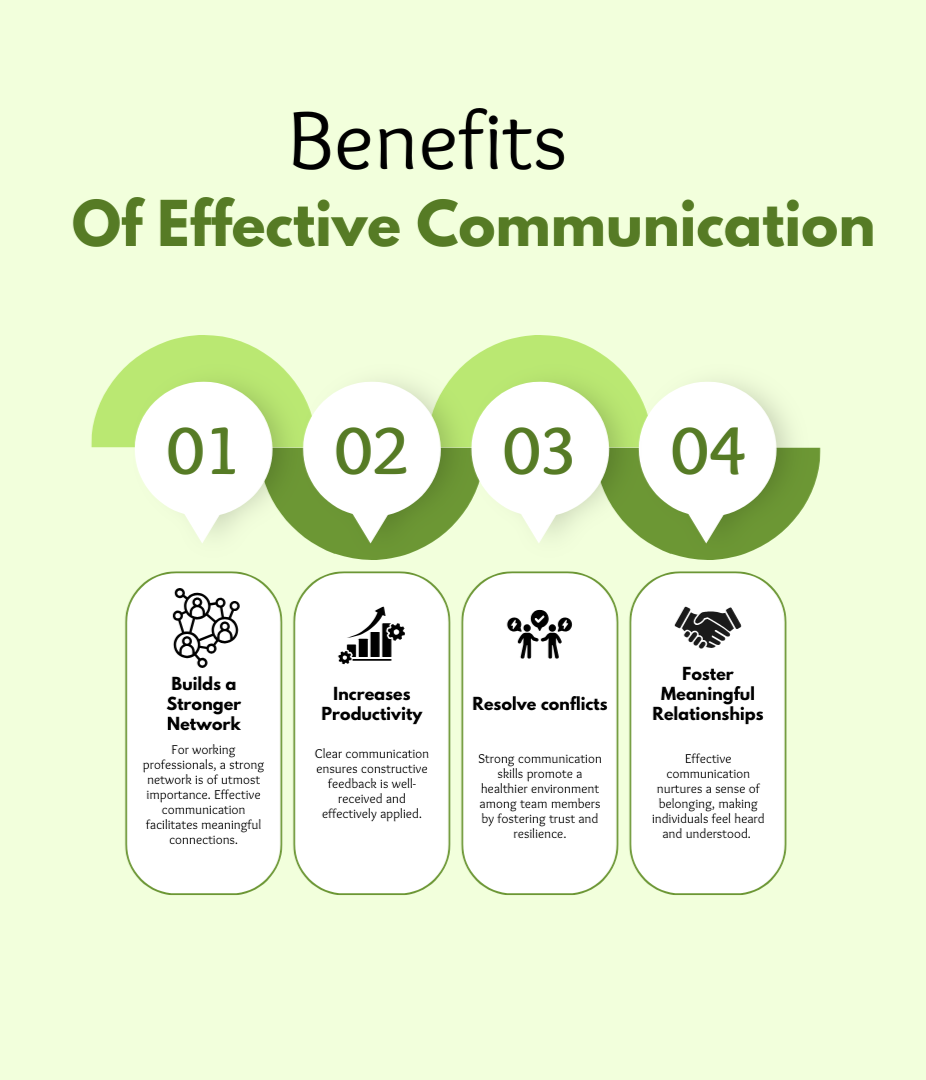
- Builds a Stronger Network: For working professionals, a strong network is of utmost importance. Effective communication facilitates meaningful connections with people who can offer guidance and open doors to professional opportunities.
- Increases Productivity: Clear communication ensures constructive feedback is well-received and effectively applied, leading to smoother project execution, enhanced job satisfaction, and increased productivity.
- Resolve conflicts: Strong communication skills promote a healthier environment among team members by fostering trust and resilience. Potential conflicts can be addressed early, preventing escalation and enabling the team to adapt and grow through challenges.
- Foster Meaningful Relationships: Effective communication nurtures a sense of belonging, making individuals feel heard and understood. This deepens emotional bonds, promotes good mental health, and enhances day-to-day productivity and well-being.
These benefits are a few of many, reflecting how effective communication is a cornerstone of professional and personal success.
Challenges of Effective Communication
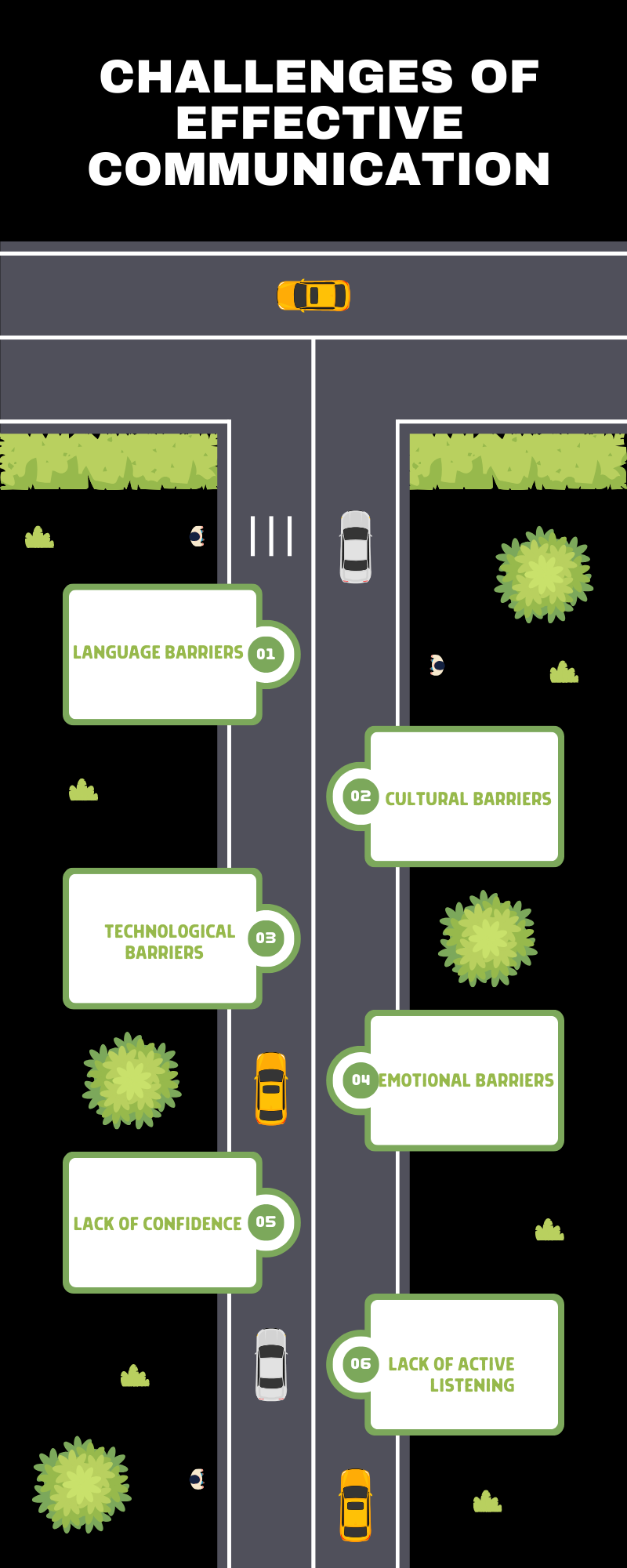
- Language Barriers: Using specific terminology or jargon can confuse the audience if they are unfamiliar with such terms. Avoiding complex language and simplifying your message improves clarity and understanding.
- Cultural Barriers: Non-verbal communication, such as gestures and body language, is interpreted differently across cultures. Misunderstandings can arise if cultural differences are not considered. Being aware of these cultural variations helps ensure your message is clear and respectful.
- Technological Barriers: Technological barriers include not being able to interpret someone’s tone over text messages or emails, which can lead to misinterpretations in communication. Sometimes poor network connections also hinder work meetings or calls, leading to incomplete and ineffective communication.
- Emotional Barriers: Emotions like anger, stress, or anxiety can interfere with rational dialogue, leading to inappropriate or unclear communication. Developing emotional intelligence helps maintain balance and ensures communication remains constructive.
- Lack of Confidence: Stage fright, shyness, or low confidence can cause individuals to stutter or struggle to articulate their thoughts effectively. This can result in misunderstandings and ineffective communication.
- Lack of Active Listening: As Stephen R. Covey aptly said, “Most people do not listen with the intent to understand; they listen with the intent to reply.” As people focus more on formulating their response rather than genuinely understanding what is being said. Failing to listen attentively leads to misinterpretation and distractions, ultimately hindering the flow of communication.
Recognizing and addressing these challenges can improve the effectiveness of communication in both personal and professional settings.
How to overcome these challenges?

1. Active Listening: Active listening involves fully focusing on what the speaker is saying to avoid misinterpretation or miscommunication.
To enhance your listening skills:
- Paraphrase: Summarize what the speaker is saying in your own words to confirm understanding. Avoid altering the core message; just restate it naturally.
- Ask questions to clarify: Do not hesitate to seek clarification. Asking thoughtful questions shows interest and ensures clear understanding.
- Maintain eye contact: Establish eye contact to convey attentiveness and respect. Try to maintain eye contact for at least 50–60% of the conversation. Aim for natural, periodic eye contact rather than staring.
- Use Affirmative Gestures: Nodding affirmatively demonstrates active engagement and encourages the speaker. It reassures them that their message is being received.
2. Provide Constructive Feedback: Exchanging feedback is essential for growth and improvement, helping others learn from experiences rather than reinventing the wheel.
How to provide constructive feedback?
- Use the I method: Instead of saying, “You made a mistake…,” say, “I noticed this could be improved.” This makes the feedback less confrontational and adds a positive tone.
- Try the Sandwich Method: Start with being positive, discuss areas for improvement, and conclude with motivation, creating a supportive atmosphere. For example, “Your hard work is commendable. A few points could use more clarity, but I’m confident you’ll address them effectively.”
How to receive feedback?
- Have a positive mindset: Approach feedback as an opportunity for growth rather than criticism. Be open to learning and improving your skills or behavior.
- Take Action: Reflect on the feedback and use it to set clear goals or implement necessary changes.
3. Adapt your communication style: Effective communication requires tailoring your approach based on your audience, context, and the situation.
- Know your audience: The first key step is to know who you are talking to. Research the demographics, interests, and expertise of your audience. Do not use jargon with the general audience; only use it with professional groups where it’s expected.
- Choose the right medium: Select the medium that best suits your message. For instance, face-to-face interactions are ideal for complex discussions. And emails are better for formal correspondence rather than an informal chat message.
- Observe reactions: Be mindful of the reactions of your audience. Non-verbal, real-time feedback helps you to steer your conversation in the right direction. If your audience looks confused, revisit your points or invite questions for better engagement.
4. Master Body Kinesics: It refers to the use of body movements, facial expressions, gestures, and posture to convey messages, emotions, and attitude. It is a vital component of nonverbal communication.
- Facial Expressions: The face is the most expressive part of the body, capable of conveying human emotions. Smiling, frowning, and raising eyebrows can be used to convey your message and intent.
- Eye contact: As the saying goes, “The eyes, chico, they never lie.” Well, yes. Maintaining eye contact builds trust and shows attentiveness. Avoiding eye contact can be interpreted as dishonesty and disinterest.
- Gestures: Hand and arm movements can enhance verbal communication. Waving to greet someone or pointing to a direction, using thumbs-up for approval, leads to better understanding.
- Posture: How you stand and sit talks a lot about you and your personality. It conveys your confidence or discomfort. For example, upright posture exudes self-assurance and interest, while a slouching posture signals fatigue or disinterest, creating an unpleasant atmosphere. Be mindful of how you carry yourself.
Conclusion:
Effective communication is a fundamental skill in all aspects of life. It is essential at every stage to achieve your goals. Fortunately, it is a skill that can be developed and refined through consistent practice and the implementation of effective strategies, which have been covered in this blog.
